ADF Architecture & Components in Azure
Introduction
ADF Architecture in azure
In the evolving cloud landscape, Azure Data Factory (ADF) plays a pivotal role in orchestrating and automating data movement and transformation. For any Azure data engineer, understanding the ADF architecture in azure and its core components is essential to build scalable and efficient data pipelines.
This blog explores the architecture, key components, and their role in a data engineering pipeline using ADF.
What is Azure Data Factory (ADF)?
Azure Data Factory is a cloud-based ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and data integration service that allows you to create data-driven workflows for orchestrating data movement and transformation.
Overview of ADF Architecture in azure
The ADF architecture in azure is designed to be modular, scalable, and cloud-native, with the following primary layers:
Pipeline Layer
Activity Layer
Integration Runtime (IR)
Linked Services
Datasets
Triggers
Monitoring & Management Layer
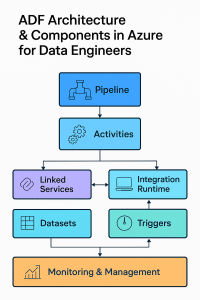
Key Components of Azure Data Factory
1. Pipeline
A logical grouping of activities that perform a task.
Example: A pipeline can ingest data from Blob Storage, transform it using Data Flow, and load it into SQL Database.
2. Activities
Tasks executed in a pipeline (e.g., Copy activity, Data Flow activity, Stored Procedure activity).
Think of them as individual ETL steps.
3. Integration Runtime (IR)
The compute infrastructure for ADF.
Three types:
Azure IR (cloud-based for data movement/flows)
Self-hosted IR (for on-premises data sources)
Azure-SSIS IR (to run SSIS packages in ADF)
4. Linked Services
Connection strings or credentials to data sources and destinations.
Like connection managers in traditional SSIS.
5. Datasets
Define schema/data structure pointing to the data within Linked Services.
Example: A dataset could represent a table in SQL or a folder in Blob Storage.
6. Triggers
Execute pipelines on schedule, event-based, or on-demand.
Useful for automation and time-based orchestration.
7. Monitoring
ADF provides detailed monitoring via the Azure portal, including:
Pipeline run history
Metrics
Alerts and logs
Mastering the ADF architecture in Azure equips Azure data engineers to build reliable, scalable, and cost-effective data pipelines. Whether you’re moving data between systems, transforming it, or loading into data warehouses, ADF is the go-to solution.
At Learnomate Technologies, we don’t just teach tools, we train you with real-world, hands-on knowledge that sticks. Our Azure Data Engineering training program is designed to help you crack job interviews, build solid projects, and grow confidently in your cloud career.
- Want to see how we teach? Hop over to our YouTube channel for bite-sized tutorials, student success stories, and technical deep-dives explained in simple English.
- Ready to get certified and hired? Check out our Azure Data Engineering course page for full curriculum details, placement assistance, and batch schedules.
- Curious about who’s behind the scenes? I’m Ankush Thavali, founder of Learnomate and your trainer for all things cloud and data. Let’s connect on LinkedIn—I regularly share practical insights, job alerts, and learning tips to keep you ahead of the curve.
And hey, if this article got your curiosity going…

Thanks for reading. Now it’s time to turn this knowledge into action. Happy learning and see you in class or in the next blog!
Happy Vibes!
ANKUSH



Comments
Post a Comment